
This is a program that provides foreign nationals with Japanese technology, skills and knowledge and thus gives them opportunities to play an active role in their home countries.
In view of its international status and role, Japan is required to contribute to the development of human ability of the people in developing countries. The Technical Intern Training Program for foreign nationals is a framework that invites talented young people from those countries to Japan in order to learn Japan's advanced technologies and knowledge, and then play an active role in the development of their home countries. (On this website, the Technical Intern Training Program for foreign nationals will often be referred to without the term "foreign nationals," such as the Technical Intern Training Program or technical interns.)
Technical Intern Training Program Was Established in 1993.
| Late 1960s | Training programs, which had been used for employee training at overseas local offices or subsidiaries of Japanese companies, began to be highly valued. |
|---|---|
| 1982 | Japanese companies started to actively invite foreign trainees from overseas. |
| 1990 | Acceptance of foreign trainees by supervising organizations began. At that time, the term "foreign trainees" was used instead of the term "technical interns." |
| 1993 | The Guidelines for Immigration Control Related to the Technical Intern Training Program" was issued by the Minister of Justice, and the Technical Intern Training Program started. (The name of "technical intern" started to be used.) |
| 2010 | The Immigration Control Act was revised, and the "Technical Intern Training" was created as a status of residence for technical interns. |
| 2016 | The Act on Proper Technical Intern Training and Protection of Technical Intern Trainees (Technical Intern Training Act) |
| 2017 | The "Organization for Technical Intern Training" was established to ensure proper implementation of the Technical Intern Training Act. |
Technical Intern Training Program Has Been Making Great Achievements.
According to Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, 1,724,328 foreign nationals were working in Japan as of the end of October 2020, of whom 23.3% were technical interns. This percentage was equivalent to 402,356 people, an increase of 4.8% from the previous year despite the impact of the Corona disaster. Among the technical interns who had returned to their home countries after completing the training period, there are many who started their own companies or became workplace leaders at Japanese-affiliate companies. They are making use of the knowledge, technology, skills, and ideas they have acquired through the training in Japan to contribute to the development of their home countries.
Technical Intern Training Program Is Not Meant to Compensate for the Labor Shortage in Japan.
The Technical Intern Training Program is not intended to solve Japan's labor shortage at a low cost, but its primary purpose is to help developing countries to secure excellent human resources of their own. To prevent the Program from being used against its original purpose, the Technical Intern Training Act contains the following two principles.
- The Technical Intern Training Program must be implemented in an environment that has been developed for the appropriate acquisition, mastery and further learning of skills, and also has been established so that the technical interns can concentrate on their technical intern training.
- The Technical Intern Training Program must not be used as a means of adjusting the supply and demand of the labor force.
How Technical Intern Training Program Works.
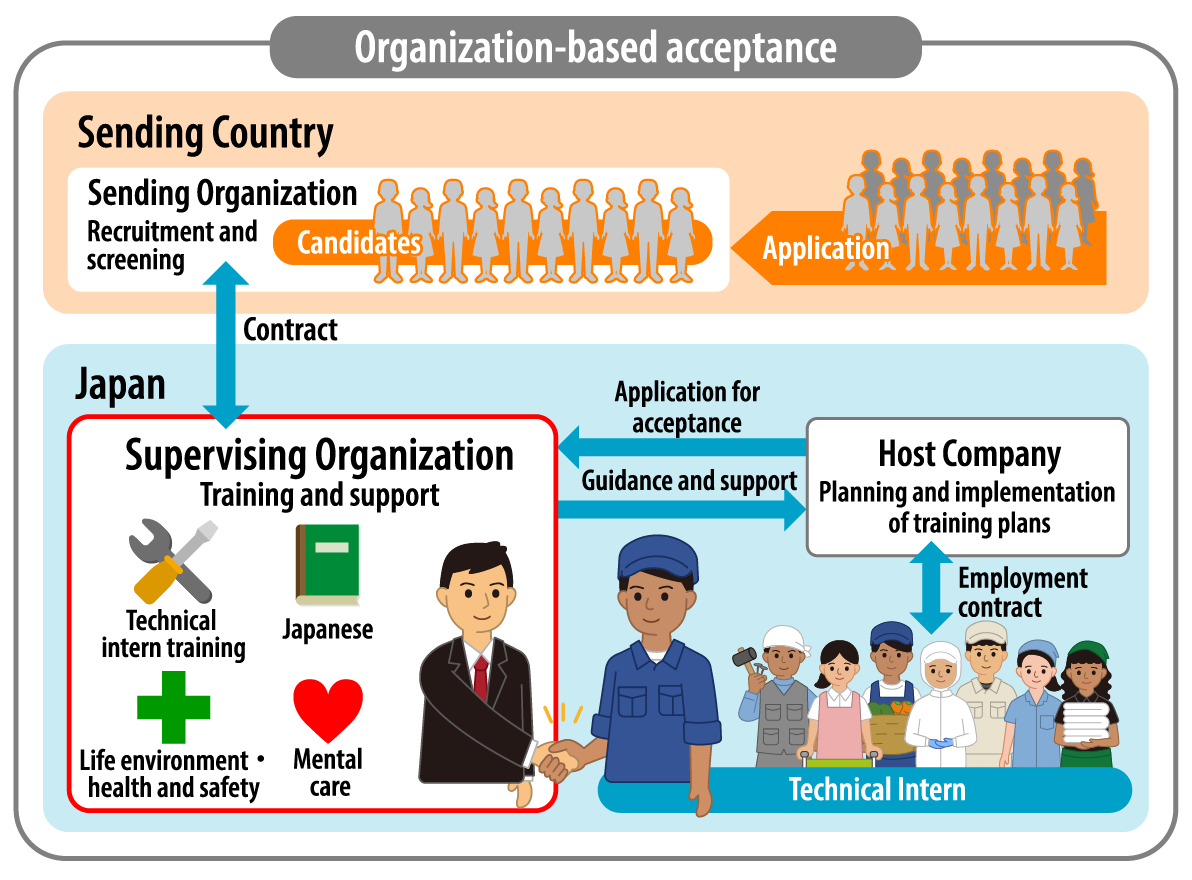
There are basically two ways to accept technical interns. One is a company-based acceptance and the other is an organization-based one.
The company-based acceptance is the one where a Japanese company itself invites and accepts local employees of its affiliated companies or business partners, or other people overseas, and provides them with training in Japan. The organization-based acceptance is managed by a supervising organization and the actual training is conducted by one of the member companies of the organization.
In many cases, the organization-based acceptance is used. This means that the technical intern training is provided through the collaboration of multiple organizations, including the sending organization in the technical interns' home country, the host company that conducts the training, the supervising organization, the Organization for Technical Intern Training, the Regional Immigration Bureau of Japan, and other relevant entities.
Flow and Stages of Technical Intern Training
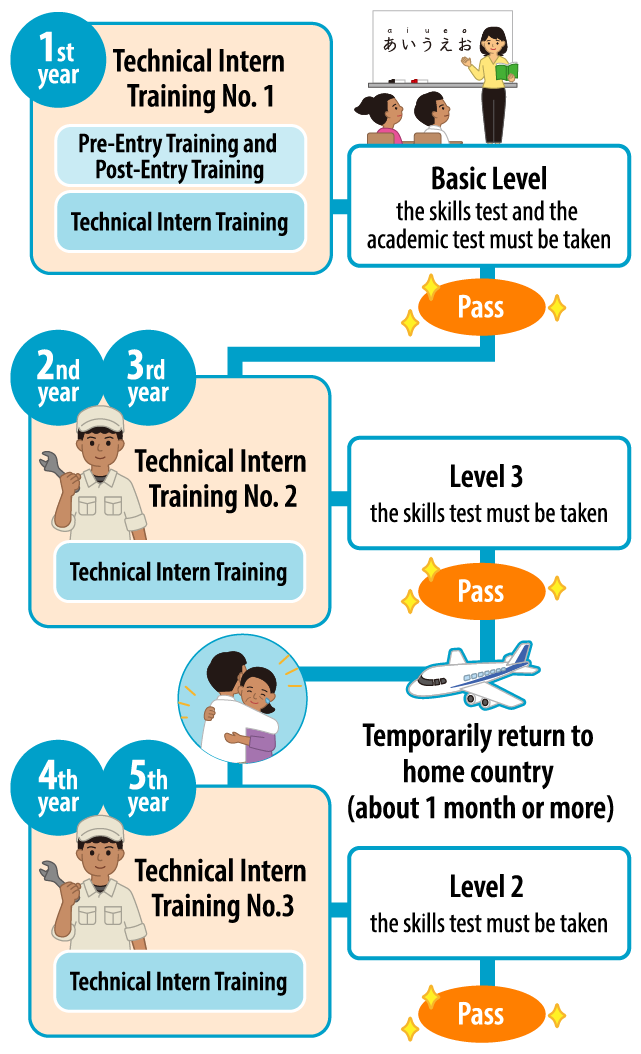
The Technical Intern Training Program is divided into several training periods, and each of these periods has a different status that is required to stay in Japan (resident status). Such periods are provided so that technical interns can properly learn everything from how to live and work in Japan to how to further improve work skills. By passing the exam at the end of each period, the technical intern can obtain the resident status required for the next training period.
| Pre-Entry Training and Post-Entry Training | After being recruited in their home country, technical interns need to complete training, where they learn Japanese language, the rules and regulations, and other information necessary to live in Japan at a local training facility. Also, after entering Japan and before being assigned to a Japanese company, they must have similar training. |
|---|---|
| Technical Intern Training No. 1 | Each of the technical interns will receive a residence card from the Immigration Bureau at the time of entry, which allows them to stay in Japan for one year, and will be assigned to a company after completing the required training. The resident status for this first year is called Technical Intern Training No. 1, and during the period, technical interns will take a skills test and a knowledge (academic) test (Skills Proficiency Test Basic Level). If they fail the test, they will lose their resident status and will not be able to continue training. |
| Technical Intern Training No. 2 | Technical interns who have passed the Skills Proficiency Test Basic Level can receive the training of Technical Intern Training No. 2 for the period of next two years. If they wish to continue the training after the period of Technical Intern Training No. 2 (two years), they must take and pass the Skills Proficiency Test Level 3 before the end of Technical Intern Training No. 2, complete the necessary procedures, and obtain the qualification for Technical Intern Training No. 3. There are some requirements or conditions to receive the training of Technical Intern Training No. 3, so please contact the nearest office of IM Japan for details. |
| Technical Intern Training No. 3 | Those who have passed the Skills Proficiency Test Level 3 (at least they must pass the skills test) can proceed to Technical Intern Training No. 3. However, they need to return to their home country (sending country) temporarily after completing Technical Intern Training No. 2, and stay there for at least one month. |
Preparations Are Required to Accept Technical Interns.
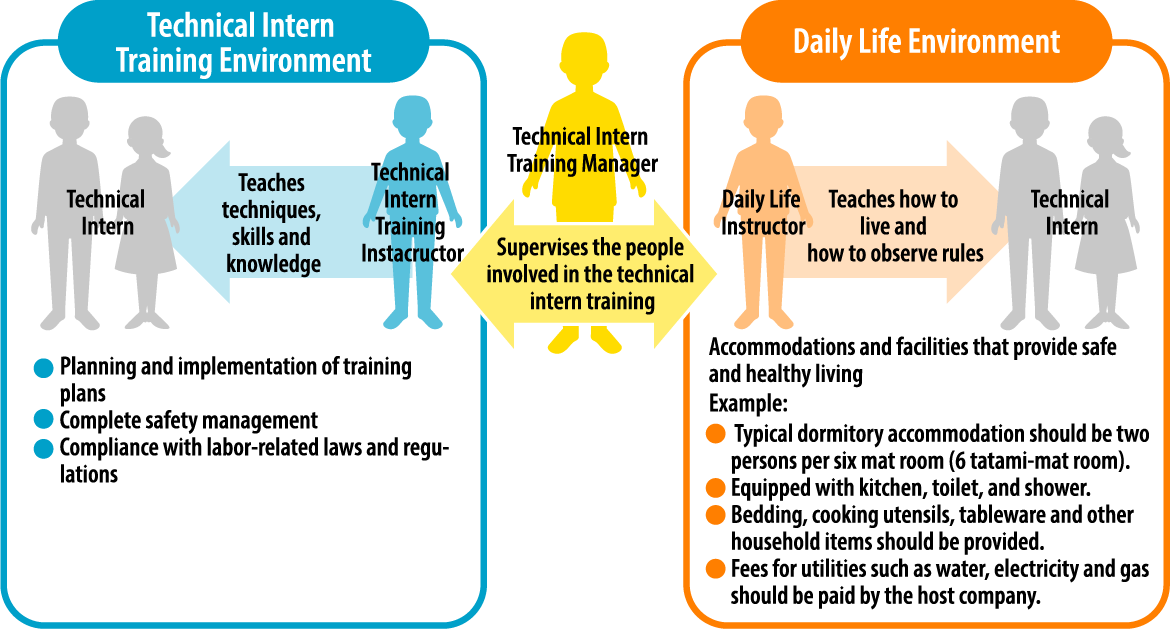
Before accepting technical interns, the company must designate three types of persons in charge and establish an environment where they can live comfortably.
| Technical Intern Training Instructor | This is a person who teaches technical interns how to work, as well as helps them to improve their skills and knowledge. This must be an experienced staff member who is familiar with the relevant job. |
|---|---|
| Daily Life Instructor | This instructor gives information such as the Japanese lifestyle and customs to technical interns whose language and values are different from the Japanese people. By doing so, the instructor helps them to live more comfortably and effectively in Japan. |
| Technical Intern Training Manager | This is a person who has completed the designated training intended to make the technical intern training safe and fruitful, and should act as a leader of staff members in charge of the technical intern training such as technical intern training instructors and daily life instructors. |
Acceptable Number of Technical Interns for Host Company
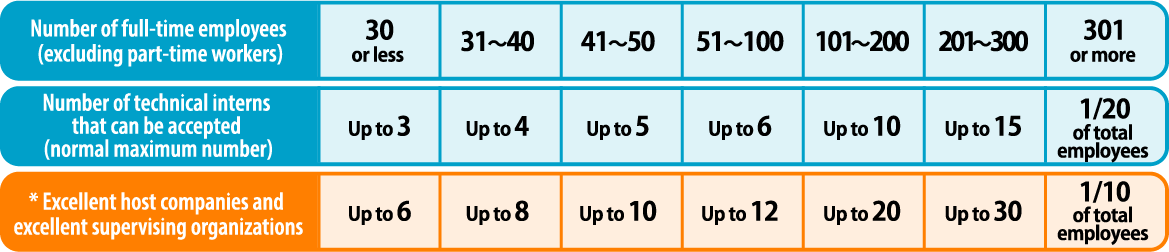
The maximum number of technical interns that a company can accept depends on the number of its employees. For example, a company with 30 employees can accept up to 3 technical interns each year. However, if a host company is recognized as an excellent one after having achieved excellent results in training technical interns, the company is allowed to accept up to twice the number mentioned above. Note that if the conditions are met, a sole proprietor can accept technical interns.
Requirements of Supervising Organizations
In addition to dispatching technical interns to host companies, a supervising organization is performing various tasks and duties, such as helping host companies to create technical intern training plans, conducting pre-entry and post-entry trainings, visiting host companies to help with their technical intern training, and counseling with technical interns in their native language. The role of a supervising organization is to support the smooth operation of the technical intern training program. So, a supervising organization must be selected by carefully considering the following points.
- Does the supervising organization accurately understand the Technical Intern Training Program, related laws, and other requirements, and strictly observe them?
- Are the administrative expenses recorded in an easy-to-understand manner, and are the amounts appropriate?
- Is the Japanese language education to their technical interns by the supervising organization proper and effective?
- Does the supervising organization carry out various procedures and services smoothly?
- Are there staff members in the supervising organization who are fluent in the native language of technical interns?
- Does the supervising organization make a periodic visit to host companies and take good care of every single one of the technical interns?
